This article provides educational information about cortisol and stress management. It is not medical advice and does not replace professional healthcare guidance. For concerns about cortisol levels or stress-related health issues, please consult a qualified healthcare provider.
What is Cortisol and How Does it Affect the Body?
Cortisol, widely recognized as the principal stress hormone, exerts extensive influence over numerous physiological processes throughout the body. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538239/)
Cortisol is a vital glucocorticoid produced by the adrenal glands. It plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions, such as regulating metabolism, reducing inflammation and controlling the sleep-wake cycle. Cortisol is integral to the body's response to stress; it alters or shuts down functions that would be nonessential or detrimental in a fight-or-flight situation.
The effects of cortisol are wide-ranging. In the short term, it helps the body respond to stress by increasing glucose in the bloodstream, enhancing the brain's use of glucose and increasing the availability of substances that repair tissues. Cortisol also curbs functions that would be nonessential in a fight-or-flight situation, such as the digestive system, the reproductive system and growth processes. This comprehensive approach of cortisol ensures that the body can react swiftly and effectively to stress.
How is Cortisol Linked to Stress and Anxiety?
Cortisol is intrinsically linked to stress and anxiety through the body's stress response system, known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. When an individual is stressed or anxious, the HPA axis is activated, leading to a surge in cortisol levels. This increase in cortisol prepares the body to handle the stressor, a process known as the ‘fight-or-flight’ response. (https://www.nichd.nih.gov/newsroom/releases/stress)
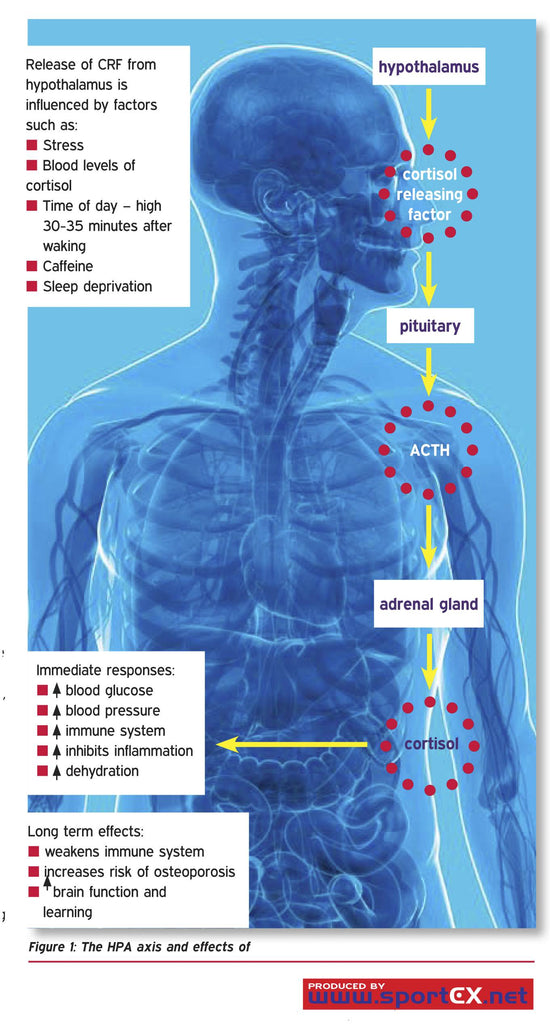
However, chronic stress can lead to prolonged cortisol elevation, which may contribute to continuous feelings of anxiety and stress. Elevated cortisol levels over long periods can disrupt almost all your body's processes, increasing the risk of numerous health problems including anxiety and mood disorders, digestive problems, heart diseases, weight gain and memory and concentration impairment.
What are the Signs of High Cortisol Levels in the Body?
High cortisol levels can manifest in various physical, psychological and behavioral signs. Physically, one may experience symptoms like rapid weight gain - mainly in the face, chest and abdomen - a flushed and round face, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, muscle weakness, increased thirst and urination. Psychologically, high cortisol levels can lead to mood swings, increased anxiety, depression and difficulties in concentration and memory.
Behaviorally, individuals might notice changes in their sleep patterns, with insomnia or interrupted sleep being common. There might also be an increase in the frequency of infections, due to the suppression of the immune system. It's important to note that these symptoms can be indicative of other health conditions and a medical professional should be consulted for an accurate diagnosis.
Can Long-Term Elevated Cortisol Levels Have Negative Health Impacts?
Yes, long-term elevation of cortisol levels can have significant negative impacts on health. Chronic high cortisol can lead to a variety of health issues, including:
- Mental health problems: such as depression, anxiety and issues with memory and concentration.
- Weight gain: particularly around the abdomen and face.
- Cardiovascular disease: including hypertension and increased risk of heart disease.
- Gastrointestinal problems: like gastritis and irritable bowel syndrome.
- Endocrine disorders: such as diabetes, due to cortisol's effect on blood sugar levels.
- Immune system suppression: leading to increased vulnerability to infections.
- Bone and muscle health: increased risk of osteoporosis and muscle weakness.
These health issues underline the importance of managing cortisol levels effectively to maintain overall health and wellbeing. (https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/stress-management/in-depth/stress/art-20046037
What Lifestyle Factors Can Lead to Changes in Cortisol Levels?
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in influencing cortisol levels. These include:
- Stress: both acute stress (such as an argument) and chronic stress (like ongoing work pressure) can elevate cortisol levels.
- Sleep patterns: poor sleep quality or an irregular sleep-wake cycle can disrupt cortisol production.
- Diet: high intake of sugar and caffeine can increase cortisol levels.
- Physical activity: both lack of exercise and excessive training can affect cortisol.
- Substance use: smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can elevate cortisol.
- Relaxation and mindset: lack of relaxation time and a negative mindset or constant worrying can increase cortisol levels.
Understanding and modifying these factors can help in balancing cortisol levels.
Are There Any Effective Strategies to Manage or Reduce High Cortisol Levels?
Managing high cortisol levels involves a holistic approach to lifestyle changes and stress management techniques. Some effective strategies include:
- Stress Management: techniques like mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises and yoga can effectively reduce stress and, in turn, cortisol levels.
- Regular Exercise: moderate exercise can help regulate cortisol, but it's important to avoid overtraining as it can increase cortisol levels.
- Balanced Diet: a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein and whole grains can help regulate cortisol. Limiting caffeine and sugar intake can also be beneficial.
- Improved Sleep Hygiene: establishing a regular sleep routine, ensuring a comfortable sleep environment and avoiding screen time before bed can improve sleep quality and regulate cortisol.
- Professional Help: counseling or therapy can be beneficial in managing chronic stress and anxiety.
- Relaxation Techniques: practices like massage, warm baths and other grounding exercises can help lower cortisol levels.
Implementing these strategies can help in effectively managing and reducing high cortisol levels.
How Does Sleep Affect Cortisol Levels and Vice Versa?
Sleep and cortisol levels have a bidirectional relationship. Cortisol levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day and night, peaking in the early morning and declining throughout the day, reaching the lowest point at midnight. Disrupted sleep patterns can lead to an imbalance in this cycle, resulting in elevated cortisol levels.
On the other hand, high cortisol levels, especially at night, can interfere with the ability to fall asleep and maintain deep sleep, leading to sleep disturbances like insomnia. This disturbance in sleep can further exacerbate the stress response and lead to even higher cortisol levels, creating a vicious cycle. Therefore, maintaining a regular sleep schedule and ensuring adequate sleep is essential for regulating cortisol levels.
Can Diet and Nutrition Play a Role in Regulating Cortisol?
Yes, diet and nutrition play a significant role in regulating cortisol levels. Certain dietary choices can help in balancing cortisol:
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: foods that have a low glycemic index such as whole grains, nuts, seeds, fruits and vegetables help in maintaining steady blood sugar levels, thereby preventing spikes in cortisol.
- Healthy Fats: omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, walnuts and flaxseeds have been shown to reduce cortisol levels.
- Protein-Rich Foods: including quality protein sources in each meal can help in managing cortisol levels.
- Hydration: adequate hydration is important for cortisol regulation.
- Limiting Caffeine and Alcohol: both substances can increase cortisol, when consumed in excess.
A balanced diet that incorporates these elements can support the body in maintaining healthy cortisol levels.
What is the Role of Exercise in Managing Cortisol Levels?
Exercise plays a complex role in cortisol regulation. Moderate exercise can help in reducing cortisol levels and improving stress resilience. Physical activity stimulates the production of endorphins, the body's natural mood elevators, which can counteract the effects of cortisol. However, it's important to balance exercise intensity and duration, as excessive or very high-intensity exercise can actually increase cortisol levels, especially if the body is not accustomed to it. Incorporating a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training and flexibility exercises, while ensuring adequate rest and recovery, can optimize the role of exercise in managing cortisol levels. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18787373/
Are There Any Specific Medical Treatments or Supplements That Can Help Regulate Cortisol Levels?
While lifestyle changes are key in managing cortisol levels, certain medical treatments and supplements may also help:
- Adaptogens: herbs like ashwagandha, rhodiola and holy basil have been claimed to help balance cortisol levels.
- Phosphatidylserine: this dietary supplement may reduce cortisol levels, particularly in response to stress.
- Medical Treatment: in cases of disorders like Cushing's syndrome or adrenal insufficiency, specific medical treatments are required to manage cortisol levels.
- Magnesium and Vitamin C: both are known to support the adrenal gland function and may help regulate cortisol.
- Mind-Body Therapies: techniques like biofeedback and acupuncture might also aid in reducing stress and balancing cortisol levels.
It's important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement or treatment for cortisol regulation.
Quick FAQ: Cortisol and Stress
Quick answers to common questions about cortisol. For detailed explanations, see the comprehensive Q&A above.
What is cortisol?
Cortisol is a glucocorticoid hormone produced by the adrenal glands, often called the "stress hormone." It regulates metabolism, reduces inflammation, controls the sleep-wake cycle, and manages the body's fight-or-flight stress response by increasing glucose availability and prioritizing essential functions during stress.
How is cortisol linked to stress and anxiety?
Cortisol is released through the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis when you experience stress or anxiety, triggering the fight-or-flight response. Chronic stress causes prolonged cortisol elevation, which can lead to persistent anxiety, mood disorders, and various health problems.
What are the signs of high cortisol levels?
Physical signs include rapid weight gain (especially in face, chest, abdomen), high blood pressure, muscle weakness, and increased thirst. Psychological symptoms include mood swings, anxiety, depression, and memory problems. Behavioral changes include sleep disturbances and frequent infections due to immune suppression.
Can high cortisol levels cause health problems?
Yes. Chronic elevated cortisol can cause mental health problems (anxiety, depression), weight gain, cardiovascular disease, gastrointestinal issues, diabetes, immune system suppression, osteoporosis, and muscle weakness. These serious health risks make cortisol management essential for overall wellbeing.
What lifestyle factors affect cortisol levels?
Major factors include chronic stress, poor sleep quality, high sugar and caffeine intake, lack of exercise or overtraining, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and constant worrying. Managing these lifestyle factors is crucial for maintaining healthy cortisol levels.
How can I reduce high cortisol levels naturally?
Effective natural strategies include stress management techniques (mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing), moderate regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in whole foods, improved sleep hygiene, limiting caffeine and sugar, relaxation practices like massage, and seeking professional counseling for chronic stress.
How does sleep affect cortisol levels?
Cortisol naturally peaks in early morning and declines throughout the day, reaching its lowest at midnight. Disrupted sleep patterns disturb this cycle, causing elevated cortisol. High nighttime cortisol interferes with falling asleep and maintaining deep sleep, creating a harmful cycle of poor sleep and high stress hormones.
Can diet help regulate cortisol levels?
Yes. Low glycemic index foods (whole grains, vegetables, fruits) maintain steady blood sugar and prevent cortisol spikes. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce cortisol levels. Quality protein at each meal, adequate hydration, and limiting caffeine and alcohol all support healthy cortisol regulation.
Does exercise help manage cortisol?
Moderate exercise reduces cortisol and improves stress resilience by stimulating endorphin production. However, excessive or very high-intensity exercise can increase cortisol levels. A balanced routine combining aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility work with adequate rest optimizes cortisol management.
Are there supplements that help regulate cortisol?
Adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha, rhodiola, and holy basil may help balance cortisol. Phosphatidylserine, magnesium, and vitamin C support adrenal function. However, always consult a healthcare professional before starting supplements, especially if you have conditions like Cushing's syndrome or adrenal insufficiency.
When should I see a doctor about cortisol levels?
Seek medical attention if you experience persistent symptoms like unexplained rapid weight gain, severe fatigue, purple stretch marks, depression, high blood pressure, or diabetes symptoms. These may indicate Cushing's syndrome or other cortisol-related disorders requiring professional medical diagnosis and treatment.
Can anxiety relief tools help with stress-related cortisol?
Yes. Sensory grounding techniques using fidget rings, textured jewelry, or calming tools can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, helping reduce stress responses and cortisol release. These tools work best when combined with other stress management strategies like mindfulness and proper sleep hygiene.
When to Seek Professional Help
While the strategies discussed here can support general wellness, professional medical evaluation is recommended if you experience:
Seek immediate medical attention if:
- Unexplained rapid weight gain (especially in face, chest, abdomen)
- Severe, persistent fatigue despite adequate rest
- Purple stretch marks on skin
- Significantly elevated blood pressure
- Signs of diabetes (excessive thirst, frequent urination)
- Symptoms of Cushing's syndrome or adrenal disorders
Schedule a consultation with your healthcare provider if:
- Stress and anxiety persist despite lifestyle changes
- Sleep problems last more than two weeks
- Mood changes interfere with daily functioning
- Physical symptoms worsen over time
- You're considering cortisol-lowering supplements
Medical Testing: Your doctor can order cortisol blood tests, saliva tests, or 24-hour urine tests to measure your cortisol levels accurately. These tests can diagnose conditions like Cushing's syndrome (too much cortisol) or Addison's disease (too little cortisol).
For personalized medical advice about cortisol management, always consult with a qualified healthcare professional.

